Sometimes we need to find sql server version number, edition or update level. People facing difficulty to determine service pack installed on they SQL Server. In this article we will explain how to query version, service pack or updates installed on SQL Server. The article using various ways to find those information of SQL Server. Sql Server Management Studio, T-SQL command, Command prompt and using query script.
- Using SQL Server Management Studio interface
- Using T-SQL command
- Check sql server version from command prompt
- Using SQL Server file exe.
- How to check sql server version using query
Find SQL Server version Query / TSQL / CMD
About SQL Server
Three main components of SQL Server version are Major Release, Service Pack Level and CU/Hotfix/Update Level. The number of SQL Server version look like 11.0.5058.0.
The first digits describe the version of SQL Server such as:
- 8.0 for SQL Server 2000
- 9.0 for SQL Server 2005
- 10.0 for SQL Server 2008
- 10.5 for SQL Server 2008 R2
- 11.0 for SQL Server 2012
- 12.0 for SQL Server 2014
- 13.0 for SQL Server 2016
The other part explains Service Pack Level and CU/Hotfix/Update Level. Find More here
Take the look on the website and search with your version number. In my case I have Service Pack 2 level update.
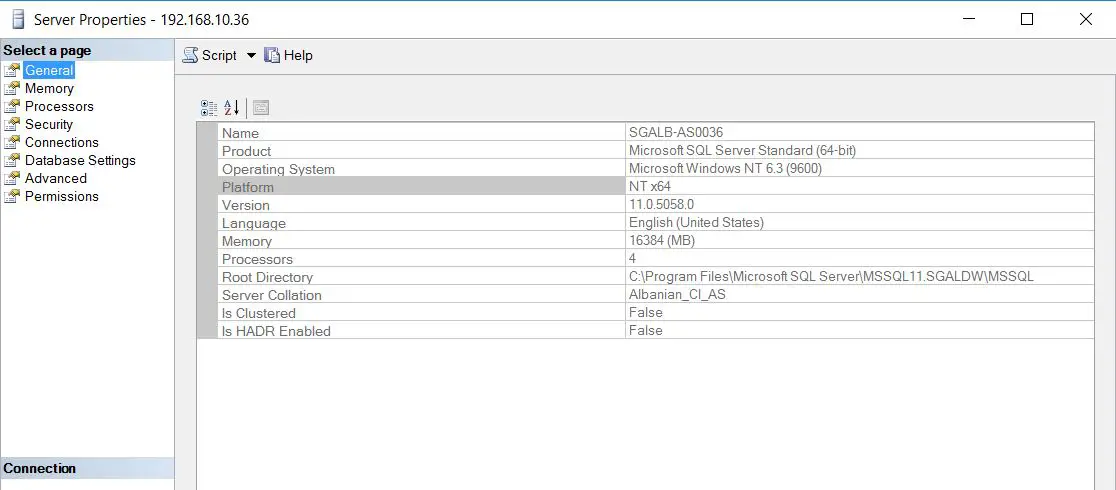
Find SQL Server Version using Management Studio Interface
- Open SQL Server Management Studio.
- Right click on the instance and select properties
- In the general section you will find information’s such:
- “Product” that give you edition version
- “Version” that give you the number of the version including Service Pack
- Other information’s like Operating system, Language, Platform etc.
Find sql server version
Get SQL Server Version using T-SQL script
Simple T-SQL script
One of the fast way to find SQL Server version is to run T-SQL script.
SELECT @@VERSION
The script will give the following information and will be the same for all products:
Microsoft SQL Server 2012 – 11.0.5058.0 (X64)
May 14 2014 18:34:29
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation
Standard Edition (64-bit) on Windows NT 6.3 (Build 9600: ) (Hypervisor)
One problem of this script is that you do not get the Service Pack.
Read also other SQL Server Helping Posts:
Other T-SQL Script
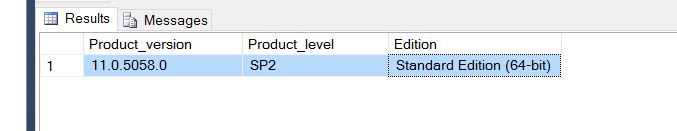
Query the SERVERPROPERTY values:
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY('productversion')AS Product_version,
SERVERPROPERTY('productlevel')AS Product_level,
SERVERPROPERTY('edition')AS Edition
Results: 11.0.5058.0 SP2 Standard Edition (64-bit)
Find sql server version query
The query will return three columns:
- The SQL Server version number
- The Service Pack Level (product level)
- Edition (enterprise, standard, web, express, etc)
To get more additional information:
select SERVERPROPERTY('MachineName')as 'Host Name',
SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') as 'Instance Name' ,
SERVERPROPERTY('IsClustered') as 'Cluster' ,
SERVERPROPERTY('Edition') as 'Edition',
SERVERPROPERTY('ProductVersion') as 'version',
SERVERPROPERTY('Productlevel') as 'Service Pack',
SERVERPROPERTY('LicenseType') as 'LicenseType' ,
SERVERPROPERTY('NumLicenses') as 'NumLicenses'
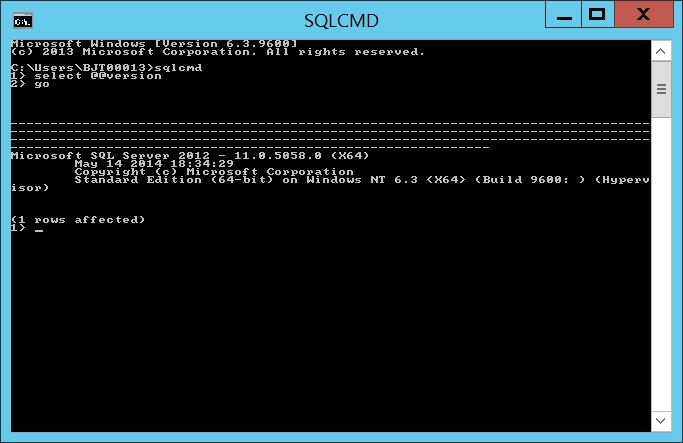
How to check sql server version from command prompt
- Launch command prompt on the SQL Server ( Start> Search CMD and click Enter)
- Type the command SQLCMD -S servername\instancename ( Change the servername and instancname)
- Or just type “SQLCMD”
- Type select @@versionand click Enter
- Type go and click Enter
SQL version will be showed on the cmd screen. Repeat the process for other instance.
How to check sql server version from command promt
Using SQL Server file exe.
This method is not very simply but is functional. Before you use this method be sure that SQL Server is not running.
- Navigate to SQL Server installed folder. For Example “C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.SGALDW\MSSQL\Binn”
- Right click on sqlservr.exe and select properties.
- Go to details tab and you will find information about SQL Server like Product name and Product Version.

get sql server version
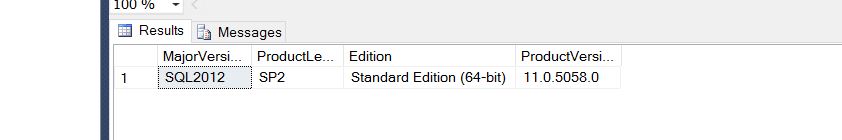
How to check sql server version using query.
The following script will return version, edition and other information’s:
SELECT
CASE
WHEN CONVERT(VARCHAR(128), SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion')) like '8%' THEN 'SQL2000'
WHEN CONVERT(VARCHAR(128), SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion')) like '9%' THEN 'SQL2005'
WHEN CONVERT(VARCHAR(128), SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion')) like '10.0%' THEN 'SQL2008'
WHEN CONVERT(VARCHAR(128), SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion')) like '10.5%' THEN 'SQL2008 R2'
WHEN CONVERT(VARCHAR(128), SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion')) like '11%' THEN 'SQL2012'
WHEN CONVERT(VARCHAR(128), SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion')) like '12%' THEN 'SQL2014'
WHEN CONVERT(VARCHAR(128), SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion')) like '13%' THEN 'SQL2016'
ELSE 'unknown'
END AS MajorVersion,
SERVERPROPERTY('ProductLevel') AS ProductLevel,
SERVERPROPERTY('Edition') AS Edition,
SERVERPROPERTY('ProductVersion') AS ProductVersion
how to check sql server version using query
Those are 5 methods to get sql server version. If you have any question feel free to ask.

